scientists revive old bulgarian recipe to make Scientists have revived an ancient Bulgarian method of yogurt-making that utilizes red wood ants to enhance fermentation.
scientists revive old bulgarian recipe to make
Historical Context of Yogurt Production
Fermenting milk to create yogurt, cheeses, and kefir is a practice that dates back thousands of years, with roots in various cultures around the globe. The methods of fermentation have often been passed down through generations, preserved in oral histories and traditional practices. Each culture has developed unique techniques and flavors, influenced by local ingredients and environmental conditions.
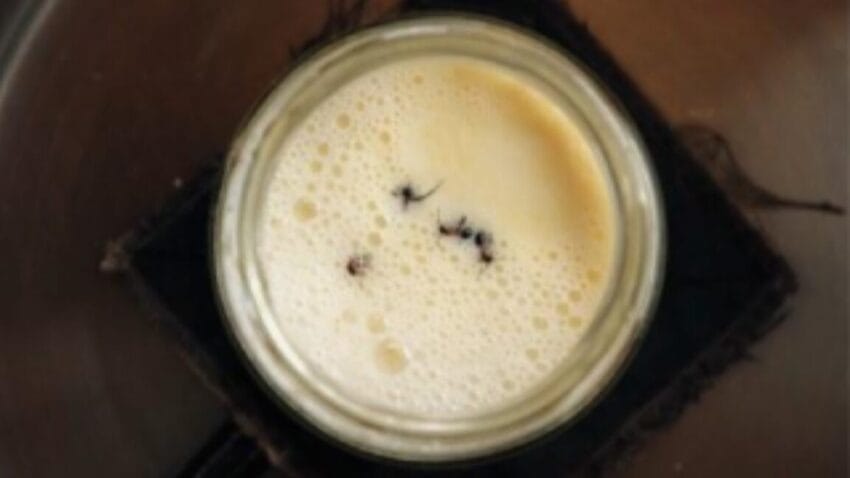
In Eastern Europe, particularly in Bulgaria and Turkey, the abundance of red wood ants has led to a distinctive yogurt-making tradition. This practice involves adding live ants or crushed ant eggs to milk, which serves as a natural catalyst for fermentation. While this method may seem unusual to modern palates, it highlights the innovative ways in which ancient communities utilized their natural surroundings to enhance food production.
Scientific Exploration of Ant-Infused Yogurt
Recent research has shed light on the effectiveness of this traditional method. A team of scientists published their findings in the journal iScience, revealing the underlying mechanisms that make ants a valuable addition to the yogurt-making process. Co-author Leonie Jahn from the Technical University of Denmark emphasized the difference between contemporary yogurt production and traditional methods. “Today’s yogurts are typically made with just two bacterial strains,” she noted. “If you look at traditional yogurt, you have much bigger biodiversity, varying based on location, households, and season. That brings more flavors, textures, and personality.”
The research team aimed to understand how the introduction of ants contributes to this biodiversity and enhances the fermentation process. By analyzing the microbial communities present in ant-infused yogurt, they discovered a rich array of bacteria and yeasts that are not typically found in modern yogurt. This diversity not only affects the flavor and texture of the yogurt but also its nutritional profile.
The Role of Ants in Fermentation
Ants are known to harbor a variety of microorganisms in their bodies, which can be beneficial for fermentation. When added to milk, these microorganisms can initiate the fermentation process, breaking down lactose into lactic acid and creating the tangy flavor associated with yogurt. The presence of these additional microbial strains can lead to a more complex flavor profile, making the yogurt richer and more varied than its commercially produced counterparts.
To explore this traditional method further, the research team collaborated with local chefs to develop modern recipes that incorporate ant yogurt. This fusion of ancient practices with contemporary culinary techniques aims to introduce a new generation to the unique flavors and health benefits of ant-infused yogurt.
Recreating the Traditional Recipe
To accurately recreate the traditional Bulgarian ant yogurt, the researchers traveled to Nova Mahala, Bulgaria, where co-author Sevgi Mutlu Sirakova’s family still resides. This location is significant, as it is a hub of culinary traditions that have been preserved over generations. The team sought guidance from Sirakova’s uncle, who provided them with the traditional instructions for making ant yogurt.
The process begins with fresh raw cow milk, which is heated until it reaches a scalding temperature—“such that it could ‘bite your pinkie finger,’” as described by the authors. This step is crucial, as it helps to eliminate any undesirable bacteria that might interfere with the fermentation process. Once the milk is prepared, four live red wood ants are collected from a nearby colony and added to the milk. The mixture is then left to ferment, allowing the ants’ microorganisms to work their magic.
Implications for Modern Culinary Practices
The revival of this ancient yogurt-making technique has broader implications for modern culinary practices and food sustainability. As consumers become increasingly interested in unique and artisanal food products, traditional methods like ant yogurt offer a way to reconnect with the past while embracing biodiversity in food production.
Moreover, the study highlights the importance of preserving traditional culinary knowledge. As globalization continues to influence food production and consumption, many local practices risk being lost. By documenting and studying these methods, researchers can help ensure that future generations have access to diverse culinary traditions.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value
In addition to its unique flavor, ant yogurt may also offer various health benefits. The diverse microbial community present in the yogurt can contribute to gut health, promoting a balanced microbiome. Fermented foods are known to be rich in probiotics, which can aid digestion and boost the immune system. The presence of additional strains of bacteria from the ants may enhance these benefits, making ant yogurt a potentially valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Furthermore, the use of local ingredients and traditional methods aligns with the growing trend of sustainable food practices. By utilizing naturally occurring resources, such as red wood ants, this method minimizes the need for artificial additives and preservatives, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Stakeholder Reactions and Future Directions
The revival of ant yogurt has garnered interest from various stakeholders, including chefs, food scientists, and cultural historians. Many chefs are excited about the potential for incorporating this unique ingredient into their menus, offering diners a taste of traditional Bulgarian culture. The collaboration between scientists and culinary experts exemplifies the potential for interdisciplinary approaches to food innovation.
Food scientists are also intrigued by the findings, as they open new avenues for research into fermentation and microbial diversity. Understanding the role of different microorganisms in food production can lead to the development of new, healthier food products that cater to evolving consumer preferences.
Cultural historians and anthropologists have expressed appreciation for the effort to document and preserve traditional culinary practices. By studying the methods used by local communities, researchers can gain insights into the cultural significance of food and its role in shaping identities.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the enthusiasm surrounding ant yogurt, there are challenges to overcome. One significant hurdle is consumer acceptance. The idea of using ants in food production may be off-putting to some, and education will be essential to help people understand the benefits and cultural significance of this practice.
Additionally, there are practical considerations regarding the sourcing of red wood ants. Ensuring a sustainable and ethical approach to harvesting these insects will be crucial to prevent overexploitation and maintain ecological balance. Researchers and producers must work together to establish guidelines that promote sustainability while preserving traditional practices.
Conclusion
The revival of the ancient Bulgarian method of making yogurt with red wood ants represents a fascinating intersection of tradition and modern science. As researchers uncover the benefits of this unique fermentation process, they not only highlight the importance of biodiversity in food production but also pave the way for a deeper appreciation of cultural culinary practices. By embracing these traditional methods, we can foster a greater understanding of food sustainability and the rich tapestry of flavors that different cultures have to offer.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: October 3, 2025 at 10:38 pm
4 views