new study highlights apple watch s role A recent study indicates that the Apple Watch could significantly enhance the monitoring of atrial fibrillation (AFib) following ablation procedures, potentially improving patient outcomes through better detection and management of the condition.
new study highlights apple watch s role
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation and Ablation
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and often rapid heartbeats. This condition can lead to various complications, including stroke and heart failure. AFib is typically managed through medication, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medical procedures such as catheter ablation. Ablation aims to destroy the areas of heart tissue that are causing the irregular electrical signals responsible for AFib.
Despite the success of ablation in restoring normal heart rhythm, patients often experience recurrences of AFib post-procedure. Monitoring these recurrences is crucial for timely intervention and management. Traditionally, this monitoring has relied on periodic check-ups and patient-reported symptoms, which can be inconsistent and may lead to missed episodes of AFib.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring AFib
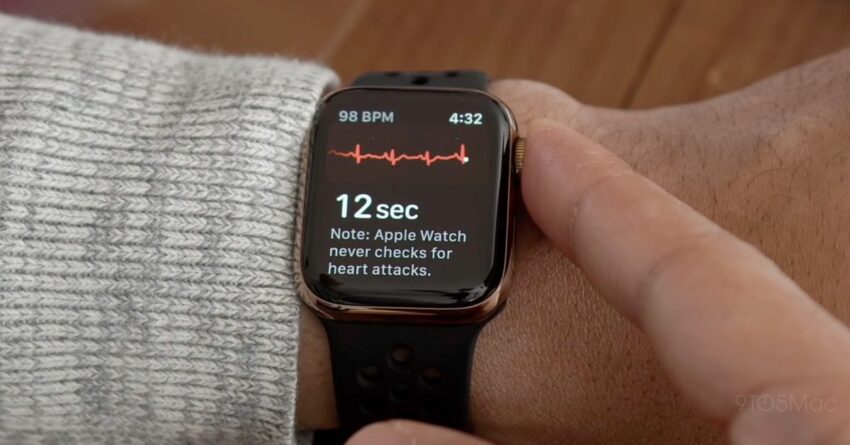
In recent years, wearable technology has emerged as a valuable tool in health monitoring. Devices like the Apple Watch are equipped with advanced sensors capable of performing electrocardiograms (ECGs), which can detect AFib episodes. The integration of such technology into patient care could revolutionize how AFib is monitored and managed, particularly after ablation.
Study Overview
The recent study focused on the impact of patient-led ECG check-ins using the Apple Watch on post-ablation outcomes. Researchers aimed to determine whether routine self-monitoring could lead to better detection of AFib recurrences and ultimately reduce the need for unplanned hospitalizations.
Conducted over a specified follow-up period, the study involved a cohort of patients who had undergone AFib ablation. Participants were instructed to regularly check their heart rhythm using the Apple Watch’s ECG feature. The results were compared to a control group that did not utilize the device for monitoring.
Findings and Implications
The findings from the study were promising. Researchers discovered that patients who engaged in regular ECG check-ins reported a higher incidence of AFib recurrences compared to those who did not monitor their heart rhythms. This increased detection rate is crucial, as it allows for timely medical intervention, potentially preventing complications associated with untreated AFib.
Moreover, the study indicated a correlation between routine monitoring and a reduction in unplanned hospitalizations. Patients who actively monitored their heart rhythms were less likely to require emergency care, suggesting that early detection and management of AFib recurrences can lead to better overall health outcomes.
Patient Empowerment Through Technology
This study underscores the importance of patient empowerment in managing chronic conditions. By utilizing wearable technology like the Apple Watch, patients can take an active role in their health care. This shift from passive to active monitoring not only enhances patient engagement but also fosters a sense of responsibility for one’s health.
Furthermore, the ability to track heart rhythms in real-time allows patients to communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers. Armed with data from their ECG check-ins, patients can provide their doctors with valuable information that can inform treatment decisions and adjustments.
Healthcare Provider Perspectives
Healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of integrating wearable technology into patient care. The study’s findings may encourage more clinicians to recommend devices like the Apple Watch to their patients, particularly those who have undergone AFib ablation.
However, it is essential for healthcare providers to educate patients on how to use these devices effectively. Proper training on interpreting ECG results and understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial to ensure that patients do not misinterpret their data or become overly anxious about benign fluctuations in heart rhythm.
Challenges and Considerations
While the study presents compelling evidence for the benefits of using the Apple Watch in post-ablation monitoring, several challenges remain. One significant concern is the accuracy of consumer-grade ECG devices compared to clinical-grade equipment. Although the Apple Watch has been validated for detecting AFib, there are instances where false positives or negatives can occur.
Additionally, not all patients may have access to or be comfortable using wearable technology. Factors such as age, technological literacy, and socioeconomic status can influence a patient’s ability to engage with these devices. Ensuring equitable access to technology will be essential in maximizing the benefits of such innovations in healthcare.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to explore the long-term implications of using wearable technology for AFib monitoring. Future studies could focus on larger, more diverse populations to assess the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, research could investigate the impact of integrating wearable data into electronic health records, allowing for more seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Another area for exploration is the potential for artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the capabilities of wearable devices. AI algorithms could analyze ECG data in real-time, providing patients and doctors with immediate insights and recommendations based on individual health profiles.
Conclusion
The recent study highlights the promising role of the Apple Watch in monitoring AFib after ablation. By enabling patients to conduct routine ECG check-ins, the device not only enhances the detection of AFib recurrences but also contributes to a decrease in unplanned hospitalizations. This shift towards patient-led monitoring represents a significant advancement in the management of atrial fibrillation.
As technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for healthcare providers, patients, and researchers to collaborate in harnessing the full potential of wearable devices. By doing so, they can improve patient outcomes and transform the landscape of chronic disease management.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: January 29, 2026 at 4:48 am
2 views















