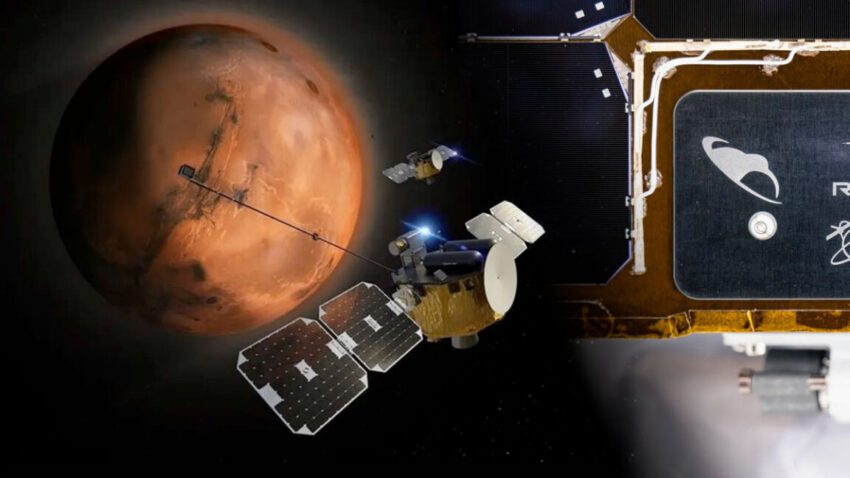
the twin probes just launched toward mars The recent launch of twin probes marks a significant milestone in Mars exploration, as they carry the first kiwis destined for the red planet.
the twin probes just launched toward mars
Overview of the ESCAPADE Mission
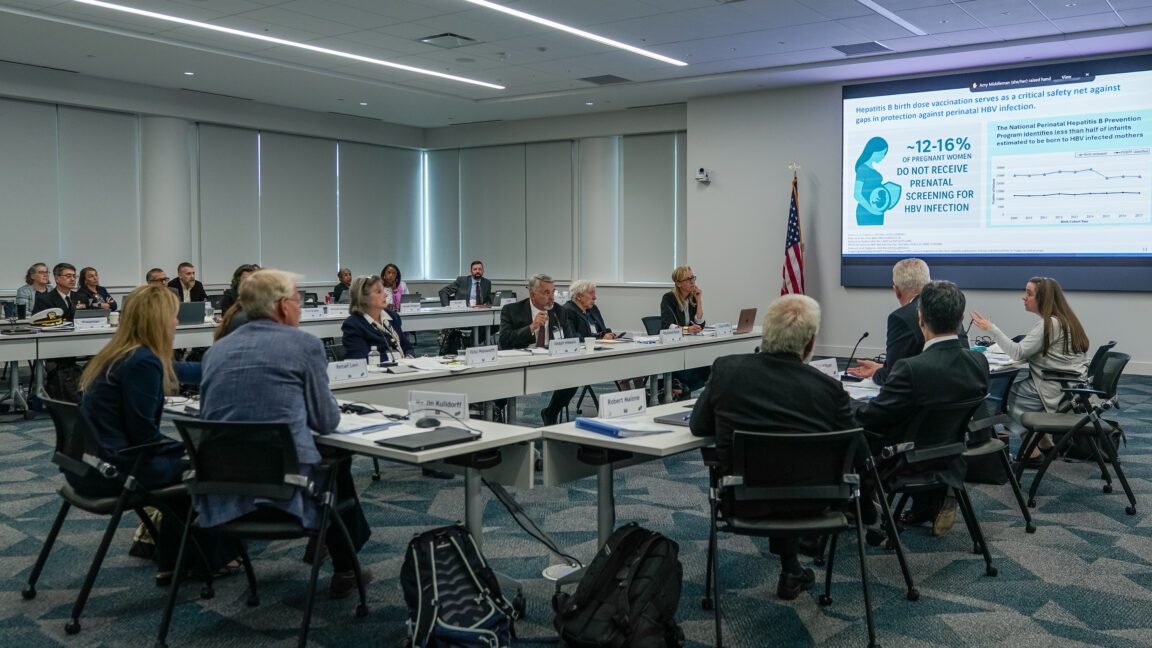
NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) mission successfully lifted off on a New Glenn rocket on Thursday, embarking on a 22-month journey to Mars. This mission is noteworthy not only for its scientific objectives but also for its innovative approach to spacecraft design and construction. The twin probes, named “Blue” and “Gold” after the colors of the University of California, Berkeley, where the mission is led, represent a collaborative effort between academic institutions and commercial space enterprises.
Scientific Objectives
The primary goal of the ESCAPADE mission is to investigate the Martian magnetosphere and how it interacts with solar wind and space weather. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for several reasons:
- Atmospheric Loss: Mars once had a dense atmosphere capable of supporting liquid water on its surface. However, over billions of years, much of this atmosphere has been stripped away, leading to the current cold and arid conditions. By studying the magnetosphere, scientists hope to uncover the mechanisms behind this atmospheric loss.
- Space Weather Effects: The mission aims to provide real-time data on how solar activity affects the Martian environment. This information is vital for future human exploration and potential colonization efforts, as it will help assess the risks posed by solar radiation.
- Planetary Comparisons: By examining Mars’ magnetosphere, researchers can draw comparisons with Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere, enriching our understanding of planetary evolution.
Technical Innovations
The ESCAPADE probes are the first Mars-bound spacecraft designed, built, and tested by Rocket Lab, a company known for its innovative approach to space technology. This collaboration highlights a growing trend in the aerospace industry, where private companies are increasingly taking on roles traditionally held by government agencies.
Rocket Lab’s end-to-end capabilities allow for a streamlined development process, which is particularly beneficial for missions with tight budgets and timelines. The ESCAPADE mission is a testament to how commercial partnerships can accelerate scientific exploration and reduce costs.
The Role of the University of California, Berkeley
The Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley, plays a pivotal role in the ESCAPADE mission. The laboratory has a long history of involvement in space science and has contributed to numerous successful missions. Its expertise in planetary science and magnetospheric studies is invaluable for the objectives of the ESCAPADE mission.
Researchers at the laboratory have designed sophisticated instruments to be deployed on the probes. These instruments will measure various parameters of the Martian environment, including magnetic fields, plasma density, and solar wind interactions. The data collected will be crucial for understanding the current state of Mars and its atmospheric history.
Collaboration with Rocket Lab
The partnership between UC Berkeley and Rocket Lab exemplifies the synergy between academia and industry. This collaboration enables the integration of cutting-edge research with practical engineering solutions. The ESCAPADE mission serves as a model for future projects, demonstrating how such partnerships can enhance scientific capabilities and expand the frontiers of space exploration.
Significance of the Launch
The launch of the ESCAPADE probes marks a historic moment in the exploration of Mars. As the first multi-spacecraft science mission to the red planet, it sets a precedent for future missions that may involve multiple spacecraft working in concert to gather data. This approach can lead to more comprehensive and nuanced understandings of planetary environments.
Moreover, the inclusion of “kiwis” on board the probes adds a unique cultural element to the mission. The term “kiwis” refers to the small, flightless birds native to New Zealand, symbolizing the involvement of Rocket Lab, which was founded in New Zealand. This aspect of the mission highlights the global nature of space exploration, where contributions come from various countries and cultures.
Future Implications
The data obtained from the ESCAPADE mission will have far-reaching implications for future Mars exploration. Understanding the processes that led to atmospheric loss will inform strategies for human colonization and the search for life on Mars. Additionally, insights into space weather interactions will be critical for ensuring the safety of astronauts and equipment on future missions.
As humanity looks toward the stars, missions like ESCAPADE will play a crucial role in preparing for long-term habitation of other planets. The knowledge gained from studying Mars can also be applied to other celestial bodies, enhancing our understanding of the solar system as a whole.
Stakeholder Reactions
The launch of the ESCAPADE mission has garnered positive reactions from various stakeholders in the scientific community. Researchers and scientists have expressed excitement about the potential discoveries that could arise from the mission. The collaboration between UC Berkeley and Rocket Lab has been particularly praised for its innovative approach to space exploration.
NASA officials have also highlighted the importance of the mission in advancing our understanding of Mars. The agency’s commitment to exploring the red planet is evident in its support for multiple missions, including the Perseverance rover and the upcoming Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the Moon as a stepping stone for future Mars missions.
Public Interest and Engagement
The ESCAPADE mission has sparked public interest in space exploration, particularly among students and young scientists. Educational outreach initiatives associated with the mission aim to inspire the next generation of explorers and researchers. By showcasing the collaborative efforts between academia and industry, the mission serves as a model for aspiring scientists and engineers.
Social media platforms have also played a role in generating excitement around the launch. NASA and Rocket Lab have utilized these platforms to share updates, behind-the-scenes content, and educational materials, engaging a broader audience in the mission’s objectives and significance.
Conclusion
The launch of the ESCAPADE probes represents a significant advancement in the exploration of Mars, combining scientific inquiry with innovative engineering. As the first multi-spacecraft mission to the red planet, it sets the stage for future explorations and deepens our understanding of planetary atmospheres and magnetospheres. The collaborative efforts between UC Berkeley and Rocket Lab exemplify the potential of partnerships in advancing space science, while the cultural significance of the mission adds an enriching layer to its narrative.
As the ESCAPADE probes make their way to Mars, the scientific community and the public alike eagerly await the insights they will provide, paving the way for future missions and the continued exploration of our solar system.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: November 15, 2025 at 3:36 am
7 views















