russia is about to do the most Russia is set to embark on an ambitious new chapter in its space exploration endeavors with the planned launch of the Russian Orbital Station (ROS), marking a significant shift in its human spaceflight program.
russia is about to do the most
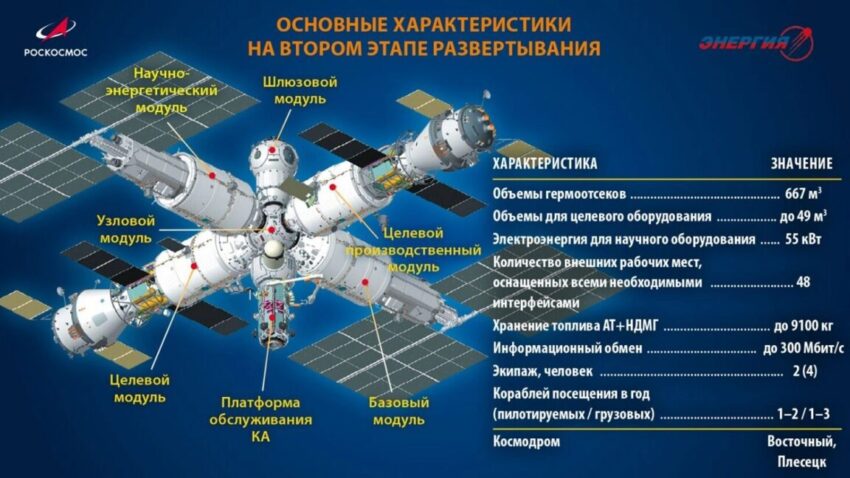
Overview of the Russian Orbital Station (ROS)
For several years, Russian officials have been vocal about their plans for the Russian Orbital Station, often highlighting its potential to serve as a cornerstone of the nation’s future in space. The ROS is envisioned as a sophisticated space station that will not only facilitate scientific research but also bolster national pride and technological prowess.
Timeline and Structure
The first elements of the ROS are scheduled for launch in 2027, with the goal of making the station ready for human habitation by 2028. This timeline reflects Russia’s commitment to re-establishing itself as a leader in space exploration, particularly as the International Space Station (ISS) approaches the end of its operational life.
Upon completion, likely in the mid-2030s, the ROS will consist of seven new modules. These modules are expected to include a variety of facilities, such as laboratories for scientific research, living quarters for astronauts, and even a private habitat designed specifically for space tourists. This inclusion of commercial space tourism aligns with global trends, where private companies are increasingly entering the space sector.
Technological Advancements
The ROS is designed to be a highly autonomous space station, capable of operating independently for extended periods. This feature is particularly significant, as it allows the station to continue functioning even in the event of communication disruptions or other unforeseen challenges. The ability to fly autonomously for months is a testament to the advanced technology that Russia aims to incorporate into the ROS.
Orbital Characteristics and National Pride
One of the most notable aspects of the ROS is its planned polar orbit at an altitude of approximately 400 kilometers. This orbital position is strategically chosen to enable the station to fly over the entirety of Russia, providing a unique opportunity for comprehensive observation of the country.
This capability is not merely a technical achievement; it carries significant implications for national pride. By establishing a space station that can monitor its own territory, Russia aims to reinforce its sovereignty in space. Furthermore, cosmonauts will no longer need to launch from Kazakhstan, as rockets will be able to take off from the Vostochny Cosmodrome, a new spaceport located in eastern Russia. This shift is expected to enhance the logistical efficiency of space missions and symbolize a new era of Russian space exploration.
Vostochny Cosmodrome: A New Era
The Vostochny Cosmodrome, inaugurated in 2016, represents a significant investment in Russia’s space infrastructure. Located in the Amur Oblast region, the spaceport was developed to reduce reliance on the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, which has been the primary launch site for Russian space missions since the Soviet era. The establishment of Vostochny is part of a broader strategy to modernize Russia’s space capabilities and enhance its autonomy in space exploration.
With the ROS, Vostochny will play a crucial role in launching missions to the new station. The ability to launch from domestic soil not only simplifies logistical operations but also serves as a point of national pride, allowing Russia to assert its independence in the realm of space exploration.
International Context and Implications
The development of the ROS comes at a time when international collaboration in space is evolving. The ISS has long been a symbol of cooperation among nations, but as its operational life nears its end, countries are exploring independent paths in space exploration. Russia’s commitment to the ROS reflects its desire to maintain a prominent position in this changing landscape.
As nations like the United States, China, and members of the European Space Agency pursue their own space initiatives, the ROS could serve as a platform for scientific research and technological innovation. The potential for collaboration with other countries or private entities remains an open question, but the ROS could become a focal point for international partnerships in space science.
Stakeholder Reactions
Reactions to the announcement of the ROS have been mixed, reflecting a range of perspectives from various stakeholders. Supporters of the project emphasize its potential to revitalize Russia’s space program and inspire a new generation of scientists and engineers. They argue that the ROS could serve as a catalyst for technological advancements and economic growth.
Conversely, critics express concerns about the feasibility of the project, particularly given Russia’s recent economic challenges and budgetary constraints. Questions have been raised about the allocation of resources to the ROS amid pressing domestic issues. Some analysts suggest that the ambitious timeline may be overly optimistic, given the complexities involved in developing and launching a new space station.
Future Prospects and Challenges
As Russia moves forward with the ROS, several challenges lie ahead. The successful development of the station will require substantial investment in research, technology, and infrastructure. Additionally, the geopolitical landscape may impact international collaboration and partnerships, which could be crucial for the station’s success.
Moreover, the global space race is intensifying, with countries like China making significant strides in their own space programs. This competition may drive innovation but could also lead to increased tensions in international relations. How Russia navigates these dynamics will be critical in determining the success of the ROS and its broader space ambitions.
Conclusion
The Russian Orbital Station represents a bold step for Russia in the realm of space exploration. With its planned launch in 2027 and aspirations for human habitation by 2028, the ROS aims to establish Russia as a key player in the future of human spaceflight. As the project unfolds, it will be essential to monitor its progress, challenges, and the implications for Russia’s role in the global space community.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: December 19, 2025 at 10:36 pm
1 views















