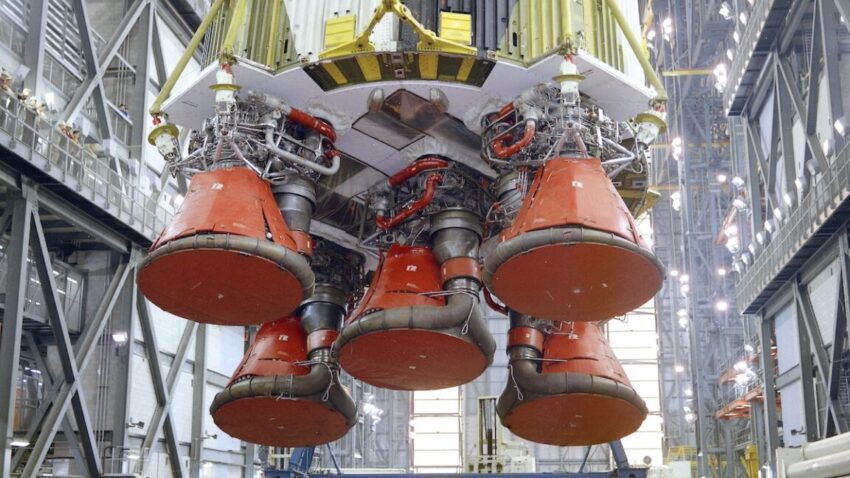
private equity deal shows just how far A recent private equity deal highlights the significant decline of America’s once-dominant rocket industry, particularly the storied legacy of Rocketdyne.
private equity deal shows just how far
Historical Significance of Rocketdyne
Rocketdyne has long been a cornerstone of the American aerospace sector, particularly noted for its pivotal role in the development of liquid-fueled rocket engines. Established in 1955 as a division of North American Aviation, Rocketdyne quickly became synonymous with innovation in rocket propulsion. The company was instrumental in the creation of engines for some of the most iconic spacecraft in history, including the Saturn V rocket that propelled astronauts to the Moon during the Apollo missions. This monumental achievement not only marked a significant milestone in human space exploration but also solidified Rocketdyne’s reputation as a leader in aerospace technology.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, Rocketdyne’s engines powered various other significant projects, including the Space Shuttle, the Atlas, Thor, and Delta rockets. The company also contributed to the development of the U.S. military’s earliest ballistic missiles, showcasing its versatility and importance in both civilian and military aerospace applications. The legacy of Rocketdyne is not merely historical; it represents a period when the United States led the world in space exploration and technological advancement.
The Decline of Rocketdyne
Despite its illustrious past, Rocketdyne’s dominance began to wane after the Cold War. The geopolitical landscape shifted, and with it, the priorities of government funding and aerospace development. The end of the Cold War meant a reduction in defense spending, which had previously bolstered many aerospace companies, including Rocketdyne. As a result, the company faced increasing competition from emerging private aerospace firms and international players.
In 1996, Rocketdyne became part of Boeing when the aerospace division of Rockwell International was acquired. This acquisition marked a significant turning point for Rocketdyne, as it transitioned from being an independent entity to a subsidiary of a larger corporation. While this change provided access to additional resources and capabilities, it also led to a shift in focus. The emphasis on large-scale rocket engine development diminished, and Rocketdyne struggled to maintain its competitive edge in a rapidly evolving industry.
Engine Development and Challenges
From the 1950s through the 1980s, Rocketdyne was prolific in designing and testing large new rocket engines. However, the post-Cold War era brought about a stark contrast. Since then, Rocketdyne has developed and qualified only one large engine design from scratch—the RS-68. This engine, which was intended for use in the Delta IV rocket, marked a significant achievement but also underscored the company’s struggles to innovate in a changing market.
The RS-68 engine was retired from service in 2024, further emphasizing the challenges Rocketdyne faced in maintaining relevance in an industry increasingly dominated by private companies. The rise of billionaires and venture capitalists investing in space exploration has transformed the landscape, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin leading the charge in innovation and cost-effective solutions. Rocketdyne, once a leader, found itself overshadowed by these new entrants.
Recent Developments: The Private Equity Deal
The recent private equity deal involving Rocketdyne has raised eyebrows and sparked discussions about the future of the company and the broader implications for the U.S. aerospace industry. This transaction appears less like a revival of a storied legacy and more akin to a corporate breakup, highlighting the fragmented state of the industry.
Details of the deal reveal that private equity firms are stepping in to acquire Rocketdyne, a move that indicates a shift in strategy. While private equity can provide necessary capital and resources, it often comes with a focus on short-term gains rather than long-term innovation. This approach raises questions about the sustainability of Rocketdyne’s operations and its ability to compete in a market increasingly characterized by rapid technological advancements.
Implications for the Aerospace Industry
The implications of this deal extend beyond Rocketdyne itself. The aerospace industry is at a crossroads, with traditional players struggling to adapt to a new era defined by private investment and commercial space exploration. The entry of private equity firms into the sector may lead to a re-evaluation of priorities, with a focus on profitability potentially overshadowing the need for innovation and long-term planning.
Moreover, the decline of legacy companies like Rocketdyne raises concerns about the future of American aerospace leadership. As private companies continue to innovate and push the boundaries of space exploration, the question remains: can traditional companies like Rocketdyne adapt to this new reality, or will they continue to fade into obscurity?
Stakeholder Reactions
The reactions from various stakeholders regarding the private equity deal have been mixed. Some industry experts view the acquisition as a necessary step for Rocketdyne to regain its footing in a competitive market. They argue that the infusion of capital from private equity could enable the company to invest in new technologies and re-establish itself as a key player in the aerospace sector.
Conversely, others express skepticism about the long-term viability of such a strategy. Critics argue that private equity firms often prioritize short-term financial returns over long-term growth and innovation. This could lead to further erosion of Rocketdyne’s capabilities and its ability to contribute meaningfully to the aerospace industry.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Rocketdyne
As Rocketdyne navigates this new chapter, the future remains uncertain. The company must grapple with the challenges of adapting to a rapidly changing industry while also addressing the legacy of its past. The question of whether Rocketdyne can leverage the resources provided by private equity to innovate and compete effectively is paramount.
Furthermore, the broader implications for the U.S. aerospace industry cannot be overlooked. As traditional companies face increasing pressure from agile private firms, the landscape is shifting. The need for collaboration between established players and new entrants may become more critical than ever. The aerospace sector must find ways to balance the strengths of legacy companies with the innovative spirit of startups to ensure continued leadership in space exploration.
Conclusion
The private equity deal involving Rocketdyne serves as a stark reminder of the challenges facing America’s legacy rocket industry. Once a leader in aerospace technology, Rocketdyne now finds itself at a crossroads, grappling with a changing landscape and the need for innovation. As the industry evolves, the future of Rocketdyne—and the broader aerospace sector—will depend on its ability to adapt and thrive in an increasingly competitive environment.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: January 7, 2026 at 2:43 am
2 views