mitm attack in apt linux package manager A recent demonstration has revealed vulnerabilities in the Advanced Package Tool (APT) used in Linux systems, showcasing a man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attack that could compromise software integrity.
mitm attack in apt linux package manager
Understanding APT and Its Role in Linux Systems
The Advanced Package Tool (APT) is a widely used package management system in Debian-based Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu. It simplifies the process of installing, upgrading, and removing software packages. APT manages dependencies and ensures that the software is up-to-date, making it an essential tool for system administrators and users alike.
APT operates by fetching packages from repositories, which are collections of software hosted on servers. These repositories are often maintained by the community or organizations, and they provide a convenient way to distribute software. However, the reliance on external sources for software updates raises concerns about security, particularly regarding the integrity of the packages being downloaded.
The MiTM Attack Demonstration
The demonstration of the MiTM attack on APT was conducted to highlight potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. In a typical MiTM attack, an attacker intercepts communication between two parties without their knowledge. In the context of APT, this means that an attacker could intercept the package download process, potentially replacing legitimate software with malicious versions.
How the Attack Works
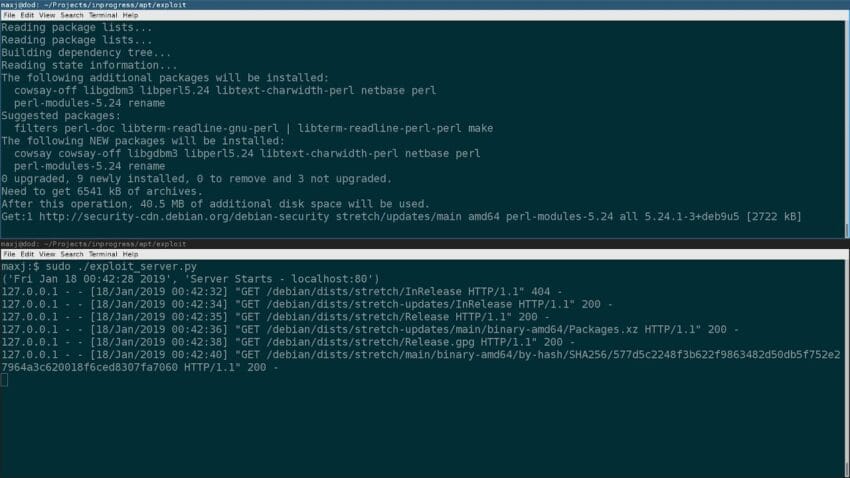
During the demonstration, the attacker set up a rogue server that mimicked a legitimate APT repository. When the victim’s system attempted to download a package, it was redirected to the attacker’s server. The attacker then had the opportunity to serve malicious software disguised as a legitimate package.
The attack exploits the fact that APT does not always verify the authenticity of the packages being downloaded. While APT can use cryptographic signatures to verify package integrity, if an attacker can intercept the initial connection, they can bypass these security measures. This highlights a critical vulnerability in the APT system that could have severe implications for users.
Technical Details of the Attack
The demonstration involved several technical steps, including:
- Setting Up a Rogue Repository: The attacker configured a server to act as a fake APT repository, mimicking the structure and content of a legitimate repository.
- Intercepting Traffic: Using tools like Wireshark and MITMf (Man-in-the-Middle Framework), the attacker intercepted the victim’s network traffic to redirect requests to the rogue server.
- Serving Malicious Packages: The attacker then served modified packages that contained malware, effectively compromising the victim’s system.
Implications of the MiTM Attack
The implications of such an attack are significant, particularly for organizations that rely on APT for software management. If attackers can successfully execute a MiTM attack, they can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, install backdoors, or even take complete control of the compromised systems.
Potential Consequences
The consequences of a successful MiTM attack on APT could include:
- Data Breaches: Attackers could exfiltrate sensitive information from compromised systems, leading to data breaches that could affect individuals and organizations.
- Malware Distribution: By serving malicious packages, attackers could spread malware across networks, leading to widespread infections and potential system failures.
- Loss of Trust: Users may lose trust in the APT system and the integrity of the software being distributed, leading to a decline in the adoption of Linux systems.
Stakeholder Reactions
The demonstration has garnered attention from various stakeholders in the cybersecurity and Linux communities. Reactions have ranged from concern to calls for immediate action to address the vulnerabilities exposed during the demonstration.
Community Response
Members of the Linux community have expressed alarm at the findings, emphasizing the need for enhanced security measures within APT. Some have suggested that APT should implement stricter verification processes for package downloads, including improved cryptographic checks and better handling of repository sources.
Industry Experts Weigh In
Cybersecurity experts have also weighed in on the implications of the demonstration. Many have pointed out that while the MiTM attack is concerning, it is not a new threat. However, the ease with which the attack was executed in the demonstration raises questions about the robustness of current security practices in package management systems.
Experts have recommended that users and organizations take proactive steps to mitigate the risks associated with MiTM attacks, including:
- Using HTTPS: Ensuring that APT repositories are accessed over HTTPS can help protect against interception.
- Regularly Updating Software: Keeping software up-to-date can help mitigate vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit.
- Implementing Network Security Measures: Utilizing firewalls and intrusion detection systems can help identify and block suspicious activity.
Mitigation Strategies
In light of the vulnerabilities demonstrated, it is crucial for users and organizations to adopt effective mitigation strategies. Here are some recommended practices to enhance security when using APT:
1. Enable HTTPS for Repositories
Ensuring that all APT repositories are accessed via HTTPS can significantly reduce the risk of interception. HTTPS encrypts the communication between the client and the server, making it more difficult for attackers to perform MiTM attacks.
2. Verify Package Signatures
APT supports the use of GPG signatures to verify the integrity of packages. Users should ensure that they are verifying package signatures before installation. This adds an additional layer of security, as it confirms that the package has not been tampered with.
3. Use Trusted Repositories
Only use repositories from trusted sources. Users should be cautious when adding third-party repositories, as these may not have the same security measures in place as official repositories.
4. Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits of systems can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are up-to-date. This includes reviewing installed packages and their sources.
5. Educate Users
Training users about the risks associated with package management and the importance of security practices can help create a more secure environment. Awareness is key in preventing successful attacks.
Conclusion
The demonstration of a MiTM attack on APT underscores the importance of security in package management systems. As Linux continues to grow in popularity, particularly in enterprise environments, the need for robust security measures becomes increasingly critical. By adopting best practices and remaining vigilant, users and organizations can mitigate the risks associated with such vulnerabilities.
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, ongoing education and adaptation will be essential in safeguarding systems against emerging threats. The Linux community must collaborate to enhance the security of APT and ensure that users can trust the software they install.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: September 8, 2025 at 6:32 pm
14 views