an explosion 92 million miles away just A significant solar event has led to the postponement of Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket launch, highlighting the intricate relationship between solar activity and space exploration.
an explosion 92 million miles away just
Impact of Solar Activity on Space Missions
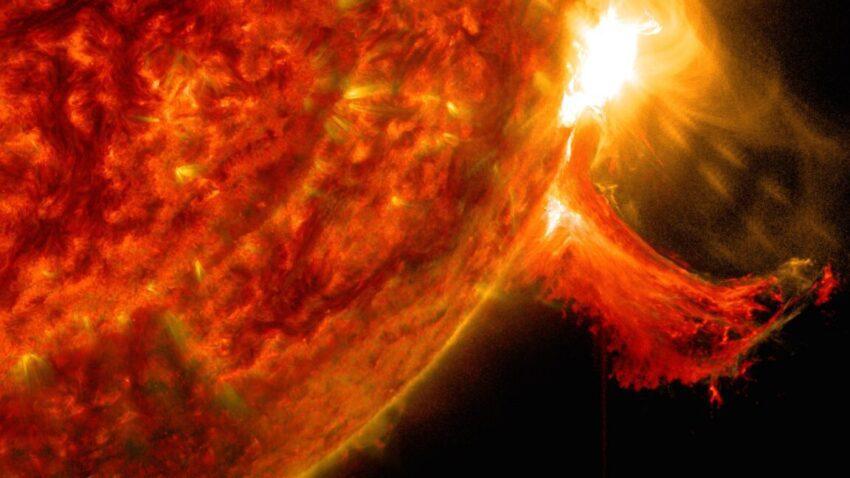
On Wednesday, a powerful wave of magnetized plasma, commonly referred to as a solar storm, surged from the Sun and enveloped the Earth. This phenomenon not only resulted in stunning auroral displays across various regions but also raised alarms regarding its potential effects on communications, navigation systems, and power grids. The implications of such solar storms extend far beyond atmospheric aesthetics; they can disrupt satellite operations and pose risks to space missions.
NASA, which is collaborating with Blue Origin for the upcoming launch, made the decision to postpone the mission due to concerns about the solar storm’s impact on the two ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft. These probes are designed to study Mars’ atmosphere and its interaction with solar winds, making them particularly vulnerable to the very solar phenomena they aim to investigate.
Details of the New Glenn Rocket Launch
The New Glenn rocket, named after the famed astronaut John Glenn, is a heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by Blue Origin. It is designed to carry a variety of payloads into orbit, including satellites and scientific instruments. The rocket’s second flight was initially scheduled for Wednesday but has now been postponed indefinitely due to the solar storm.
Blue Origin has been working diligently to establish New Glenn as a reliable option for both commercial and governmental space missions. The rocket is notable for its reusable first stage, which is intended to reduce the cost of access to space. However, the recent solar storm has underscored the challenges that even the most advanced rocket systems face when external environmental factors come into play.
Understanding Solar Storms
Solar storms are caused by the Sun’s activity, particularly during periods of heightened solar activity known as solar cycles. These storms can release large amounts of energy and charged particles into space, which can interact with the Earth’s magnetic field. The result is a range of phenomena, from beautiful auroras to potential disruptions in technology.
Solar storms can affect satellite operations in several ways:
- Communication Disruptions: Satellites rely on radio waves to transmit data back to Earth. Solar storms can cause fluctuations in the ionosphere, leading to degraded signal quality or complete communication blackouts.
- Navigation System Impacts: Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites can experience inaccuracies during solar storms, affecting navigation for both civilian and military applications.
- Power Grid Vulnerabilities: The charged particles from solar storms can induce currents in power lines, potentially leading to transformer damage and widespread power outages.
The recent solar storm has prompted not only NASA but also other space agencies and organizations to reevaluate their launch schedules and operational protocols. The unpredictability of solar activity poses a constant challenge for mission planners, requiring them to remain agile and responsive to changing conditions.
NASA’s ESCAPADE Mission
The ESCAPADE mission aims to send two spacecraft to Mars to study its atmosphere and the processes that shape it. Understanding Mars’ atmosphere is crucial for several reasons, including the planet’s potential for past life and its suitability for future human exploration.
The ESCAPADE spacecraft will investigate how solar winds interact with Mars’ atmosphere, which is significantly thinner than Earth’s. This interaction can lead to atmospheric loss, a critical factor in understanding the planet’s climatic history. The data collected by these probes will contribute to a broader understanding of planetary atmospheres and their evolution, not just on Mars but across the solar system.
Stakeholder Reactions
The decision to postpone the launch has elicited a range of reactions from stakeholders involved in the mission. Blue Origin expressed its commitment to safety and the importance of ensuring optimal conditions for the launch. In a statement, the company emphasized that the decision was made in collaboration with NASA and was in the best interest of the mission’s success.
NASA officials echoed this sentiment, highlighting the need for caution when dealing with solar phenomena. “The safety of our spacecraft and the integrity of our mission are our top priorities,” said a NASA spokesperson. “We will continue to monitor solar activity and will reschedule the launch when conditions are favorable.”
Industry experts have also weighed in on the implications of the postponement. Some have pointed out that while solar storms are a natural occurrence, their increasing frequency and intensity may be linked to broader changes in the solar cycle. This raises questions about how space agencies and private companies can better prepare for such events in the future.
Future Considerations for Space Exploration
The postponement of the New Glenn launch serves as a reminder of the challenges that come with space exploration. As missions become more ambitious and technology advances, the need for robust contingency plans becomes increasingly critical. Space agencies and private companies must invest in research and development to better understand solar activity and its effects on space missions.
In addition to improving forecasting models for solar storms, there is a growing need for enhanced shielding and protective measures for spacecraft. This includes designing satellites and probes that can withstand the effects of solar radiation and charged particles. Such advancements will be essential for ensuring the safety and success of future missions, particularly those aimed at exploring distant planets and moons.
The Broader Context of Space Exploration
The postponement of the New Glenn rocket launch is not an isolated incident but part of a larger narrative in the realm of space exploration. As more private companies enter the space industry, the competition for launch contracts intensifies. Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos, is one of several companies vying for a share of the lucrative space launch market, which includes government contracts and commercial satellite deployments.
The landscape of space exploration is rapidly evolving. With missions to Mars, lunar exploration, and the potential for human settlement on other celestial bodies, the stakes have never been higher. The interplay between solar activity and space missions will continue to be a critical factor in mission planning and execution.
Looking Ahead
As the space community awaits the rescheduling of the New Glenn launch, attention will turn to how Blue Origin and NASA respond to the challenges posed by solar storms. The ability to adapt and innovate in the face of such natural phenomena will be crucial for the success of future missions.
In the meantime, the scientific community will continue to monitor solar activity and its implications for both Earth and space exploration. Understanding the Sun’s behavior not only enhances our knowledge of our solar system but also informs our preparedness for potential disruptions that could affect life on Earth.
Ultimately, the postponement of the New Glenn launch serves as a reminder of the complexities and uncertainties inherent in space exploration. As we venture further into the cosmos, the lessons learned from events like this will shape the future of our endeavors beyond Earth.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: November 13, 2025 at 3:37 am
6 views