four-inch worm hatches in woman s forehead A recent medical case in Romania has drawn attention after doctors successfully removed a living, four-inch roundworm from a woman’s eyelid, highlighting the unusual and sometimes alarming consequences of parasitic infections.
four-inch worm hatches in woman s forehead
Case Overview
The incident, reported in the New England Journal of Medicine, involved a 32-year-old woman who initially noticed a hard lump in her right temple about a month before the worm’s emergence. This lump, which she described as a nodule, was not painful and seemed to disappear just a day before the worm made its way to her eyelid. The sequence of events leading to the discovery of the worm underscores the complexities of diagnosing parasitic infections.
Initial Symptoms
According to the woman’s account, she first observed the nodule in her temple without any accompanying symptoms. This lack of pain or discomfort may have contributed to her decision to delay seeking medical attention. However, the sudden disappearance of the lump raised concerns, prompting her to consult an ophthalmologist when she noticed the unusual movement in her eyelid.
Medical Examination
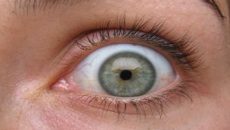
Upon examination, the ophthalmologist identified a “mobile lesion” on the woman’s left eyelid. The lesion exhibited a distinct shape that resembled a bunched-up worm just beneath the skin, accompanied by mild redness and swelling. This visual cue was critical in guiding the medical team toward the correct diagnosis. The presence of a live parasite in such a visible area of the body is both rare and alarming, prompting immediate action from the healthcare professionals involved.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Following the initial examination, the medical team proceeded with a series of diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of the worm. The diagnosis was confirmed as a case of cutaneous larva migrans, a condition caused by the migration of parasitic larvae through the skin. This condition is typically associated with certain types of roundworms, which can infect humans through contact with contaminated soil or surfaces.
Removal Procedure
Once the diagnosis was confirmed, the medical team prepared for the removal of the worm. The procedure was performed under local anesthesia, ensuring the patient remained comfortable throughout the process. The doctors carefully excised the area around the worm, allowing for its safe extraction. The entire procedure was conducted with precision, as the team aimed to minimize any potential damage to the surrounding tissues.
Post-Removal Care
After the successful removal of the worm, the woman was monitored for any signs of infection or complications. Post-operative care is crucial in such cases, as the risk of secondary infections can increase following the removal of a parasite. The medical team provided the patient with instructions on how to care for the incision site and signs to watch for that might indicate complications.
Understanding Parasitic Infections
This case serves as a reminder of the potential risks associated with parasitic infections, particularly in regions where such infections are more prevalent. Parasitic worms can enter the human body through various routes, including ingestion, skin contact, or insect bites. Understanding how these infections occur is essential for prevention and early detection.
Types of Parasitic Worms
There are several types of parasitic worms that can affect humans, including:
- Roundworms: These are cylindrical worms that can live in various parts of the body, including the intestines and tissues.
- Flatworms: These include tapeworms and flukes, which can also cause significant health issues.
- Hookworms: These worms attach to the intestinal wall and can lead to anemia and malnutrition.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Parasitic infections can be transmitted through several means, including:
- Contaminated Food and Water: Consuming undercooked or contaminated food can introduce parasites into the digestive system.
- Soil Contact: Certain parasites can penetrate the skin when individuals come into contact with contaminated soil.
- Insect Bites: Some parasites are transmitted through bites from infected insects.
Risk factors for parasitic infections include poor sanitation, lack of access to clean water, and living in or traveling to areas where such infections are common. Awareness and education are vital in reducing the incidence of these infections.
Implications for Public Health
The case of the woman in Romania highlights the need for increased awareness of parasitic infections and their potential consequences. Public health initiatives aimed at educating communities about prevention methods can play a crucial role in reducing the incidence of such infections.
Preventive Measures
To mitigate the risk of parasitic infections, individuals can take several preventive measures:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing, especially after handling soil or before eating, can help prevent infections.
- Ensure Food Safety: Cooking food thoroughly and avoiding contaminated water sources are essential steps in preventing parasitic infections.
- Avoid Skin Contact with Contaminated Soil: Wearing shoes and protective clothing when in areas where parasites are known to thrive can reduce the risk of infection.
Healthcare System Response
Healthcare systems must be prepared to recognize and treat parasitic infections effectively. This includes training healthcare professionals to identify symptoms early and provide appropriate treatment options. Additionally, public health campaigns can raise awareness about the risks associated with parasitic infections and promote preventive measures.
Reactions from the Medical Community
The medical community has responded to this case with a mix of concern and intrigue. Many healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and treatment in preventing complications associated with parasitic infections. The unusual nature of this case has sparked discussions about the need for further research into the prevalence of such infections and their impact on public health.
Patient Education
Educating patients about the signs and symptoms of parasitic infections is crucial. Individuals should be aware of any unusual lumps or lesions on their bodies and seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
The case of the woman from Romania serves as a stark reminder of the potential dangers posed by parasitic infections. While such cases are rare, they underscore the importance of vigilance and awareness in preventing and treating these infections. Public health initiatives aimed at education and prevention can play a vital role in reducing the incidence of parasitic infections and ensuring that individuals receive timely and effective treatment when needed.
Source: Original report
Was this helpful?
Last Modified: November 28, 2025 at 6:37 am
4 views















